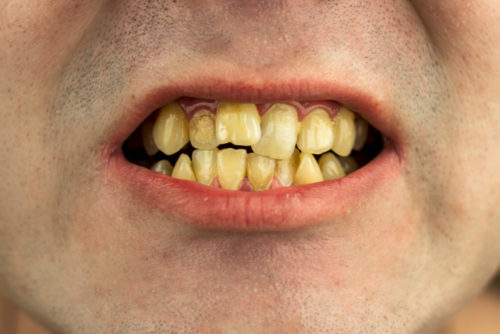
Otherwise known as tartar or calculus, calcium deposits are hardened patches of plaque that form on the teeth. If allowed to remain, plaque, a naturally occurring layer of bacteria found on tooth enamel, progresses to form visible calcium deposits. Typically, tartar arises in hard-to-reach areas of the teeth, especially along the gum line and between the teeth. Calcium deposits can still form even if you take excellent care of your teeth. Once calcium builds up on teeth, you can’t remove it by brushing. If left untreated, it can cause tooth decay. For more information on why your teeth look calcified and how to treat it, please read on, then contact one of our experienced general dentistry dentists located in Basking Ridge and Morristown, NJ as soon as possible.
What are the signs and symptoms of calcified teeth?
Despite being an asymptomatic cosmetic issue at first, calcium buildup can lead to a range of health issues. The primary signs of calcium deposits include:
- Yellowish, brown or dark color
- Textured feel and/or fuzziness when running your tongue over your teeth
- Chronic halitosis, i.e. bad breath
- Bloody, red gums and/or bleeding after brushing or flossing
What could calcium deposits on your teeth develop into?
Much more serious dental issues can arise if left untreated, including:
- Gingivitis, i.e. gum disease
- Periodontitis, i.e. gum infection
- Gum recession
- Cavities
- Tooth loss
- Tooth abscess and infection
How do you remove calcium deposits on your teeth?
Once formed, only your dentist can remove calcium deposits. Dentists rely on multiple procedures to remove tartar, including:
- Scaling: This involves using specialized tools – such as ultrasonic scrapers, which vibrate at a very high rate and shoot water to get rid of tartar – to physically remove calcium deposits and plaque from your teeth.
- Polishing: After scaling and cleaning your teeth, your dentist or hygienist will smooth out rough areas of enamel and provide a final deep clean.
- Scaling and root planing: In more difficult cases, your dentist will need to engage in invasive deep cleaning, which will require an anesthetic, to take on calcium deposits further below the gum line and at the roots of teeth and around bone.
How do you prevent calcified teeth?
Proper dental hygiene is the key to preventing calcium deposits. Effective, regular tooth care can get rid of plaque, stopping it from developing into tartar. That means you should:
- Brush properly: For two minutes at a time twice a day, you should brush thoroughly and properly.
- Flossing: At least once a day, you should gently, but thoroughly work to pull food and plaque from surfaces brushing can’t access. For those reluctant to use string, perhaps try a water irrigation system, such as the Water Pik.
- Eating habits: A balanced diet helps maintain healthy teeth and gums, so steer clear of sugary sodas, candies and other sweets.
- Regular dental visits: Get check-ups from our team twice a year to prevent calcium deposits from forming in certain areas.
Contact The Dental Associates of Basking Ridge
Please contact us today to schedule an appointment if you have any dental issues.






